4D v16.3
INTERSECTION
 INTERSECTION
INTERSECTION
| INTERSECTION ( set1 ; set2 ; resultSet ) | ||||||||
| Parameter | Type | Description | ||||||
| set1 | String |

|
First set | |||||
| set2 | String |

|
Second set | |||||
| resultSet | String |

|
Resulting set | |||||
INTERSECTION compares set1 and set2 and selects only the records that are in both. The following table lists all possible results of a set Intersection operation.
| Set1 | Set2 | Result Set |
| Yes | No | No |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| No | Yes | No |
| No | No | No |
The graphical result of an Intersection operation is displayed here. The shaded area is the result set.
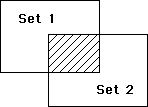
The resultSet is created by INTERSECTION. The resultSet replaces any existing set having the same name, including set1 and set2. Both set1 and set2 must be from the same table. The resultSet belongs to the same table as set1 and set2. If the same current record is set in both set1 and set2, it remains memorized in the resultSet. Otherwise, resultSet does not have a current record.
4D Server: In Client/Server mode, sets are "visible" depending on their type (interprocess, process and local) and where they were created (server or client). INTERSECTION requires all three sets to be visible on the same machine. See the 4D Server, Sets and Named Selections section in the 4D Server Reference manual for more information.
The following example finds the customers who are served by two sales representatives, Joe and Abby. Each sales representative has a set that represents his or her customers. The customers that are in both sets are represented by both Joe and Abby:
INTERSECTION("Joe";"Abby";"Both") ` Put customers in both sets in Both
USE SET("Both") ` Use the set
CLEAR SET("Both") ` Clear this set but save the others
DISPLAY SELECTION([Customers]) ` Display customers served by both
Product: 4D
Theme: Sets
Number:
121
Created: < 4D v6
4D Language Reference ( 4D v16)
4D Language Reference ( 4D v16.1)
4D Language Reference ( 4D v16.2)
4D Language Reference ( 4D v16.3)











