4D v14.3
JSON Stringify
 JSON Stringify
JSON Stringify
| JSON Stringify ( value {; *} ) -> Function result | ||||||||
| Parameter | Type | Description | ||||||
| value | Object, Object array, String, Real, Date, Time |

|
Data to convert into JSON string | |||||
| * | Operator |

|
Pretty printing | |||||
| Function result | Text |

|
String containing serialized JSON text | |||||
The JSON Stringify command converts the value parameter into a JSON string. This command serializes data into JSON; it performs the opposite action of the JSON Parse command.
Pass the data to be serialized in value. It can be expressed in scalar form (string, number, date or time) or by means of a 4D object (or an object array).
In the case of an object, you can include all types of values (see the JSON data types paragraph). JSON formatting must respect the following rules:
- String values must be enclosed in quotes. All Unicode character can be used except for special characters that must be preceded by a backslash.
- Numbers: interval of ±10.421e±10
- Booleans: "true" or "false" strings
- Pointers to a field, variable or array (the pointer is evaluated when it is stringified)
- Dates: Text type
- Times: Real type
You can pass the optional * parameter to include formatting characters in the resulting string. This improves the presentation of JSON data (known as pretty formatting).
Conversion of scalar values:
$vc:=JSON Stringify("Eureka!") // "Eureka!"
$vel:=JSON Stringify(120) // "120"
$vd:=JSON Stringify(!28/08/2013!) // "2013-08-27T22:00:00Z"
$vh:=JSON Stringify(?20:00:00?) // "72000000" seconds since midnightConversion of a string containing special characters:
$s:=JSON Stringify("{\"name\":\"john\"}")
// $s="{\\"name\\":\\"john\\"}"
$p:=JSON Parse($s)
// $p={"name":"john"}Example using a pointer to a variable:
C_OBJECT($MyTestVar)
C_TEXT($name ;$jsonstring )
OB SET($MyTestVar;"name";->$name) // object definition
// $MyTestVar= {"name":"->$name"}
$jsonstring :=JSON Stringify($MyTestVar)
// $jsonstring ="{"name":""}"
//...
$name:="Smith"
$jsonstring :=JSON Stringify($MyTestVar)
//$jsonstring = "{"name" : "Smith"}"Serialization of a 4D object:
C_TEXT($varjsonTextserialized)
C_OBJECT($Contact)
OB SET($Contact;"firstname";"Alan")
OB SET($Contact;"lastname";"Monroe")
OB SET($Contact;"age";40)
OB SET($Contact;"phone";"[555-0100,555-0120]")
$varjsonTextserialized:=JSON Stringify($Contact)
// $varjsonTextserialized = "{"lastname":"Monroe","phone":"[555-0100,
// 555-0120]","age":40,"firstname":"Alan"}"Examples of serializing a 4D object with and without the * parameter:
C_TEXT($MyContact)
C_TEXT($MyPContact)
C_OBJECT($Contact;$Children)
OB SET($Contact;"lastname";"Monroe";"firstname";"Alan")
OB SET($Children;"firstname";"Jim";"age";"12")
OB SET($Contact;"children";$Children)
$MyContact:=JSON Stringify($Contact)
$MyPContact:=JSON Stringify($Contact;*)
//$MyContact= {"lastname":"Monroe","firstname":"Alan","children":{"firstname":"John","age":"12"}}
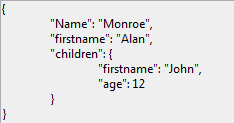
//$MyPContact= {\n\t"lastname": "Monroe",\n\t"firstname": "Alan",\n\t"children": {\n\t\t"firstname": "John",\n\t\t"age": "12"\n\t}\n}The advantage of this formatting is clear when the JSON is shown in a Web area:
- Standard formatting:

- Pretty formatting:
Product: 4D
Theme: JSON
Number:
1217

Created: 4D v14
JSON Parse
JSON Stringify array
4D Language Reference ( 4D v14 R2)
4D Language Reference ( 4D v14 R3)
4D Language Reference ( 4D v14.3)
4D Language Reference ( 4D v14 R4)







