4D v18
Description of log files
- 4D Design Reference
-
- Debug log files
-
- Description of log files
 Description of log files
Description of log files
4D applications can generate several log files that are useful for debugging or optimizing their execution. Logs are usually started or stopped using selectors of the SET DATABASE PARAMETER or WEB SET OPTION commands and are stored in the Logs folder of the database (see the Description of 4D files section).
Information logged needs to be analyzed to detect and fix issues. This appendix provides a comprehensive description of the following log files:
- 4DRequestsLog.txt
- 4DRequestsLog_ProcessInfo.txt
- HTTPDebugLog.txt
- 4DDebugLog.txt
- 4DSMTPLog.txt
- ORDA client requests log file
These log files share some fields so that you can establish a chronology and make connections between entries while debugging:
- sequence_number: this number is unique over all debug logs and is incremented for each new entry whatever the log file, so that you can know the exact sequence of the operations.
- connection_uuid: for any 4D process created on a 4D client that connects to a server, this connection UUID is logged on both server and client side. It allows you to easily identify the remote client that launched each process.
This log file records standard requests carried out by the 4D Server machine or the 4D remote machine that executed the command (excluding Web requests).
How to start this log:
- on the server:
SET DATABASE PARAMETER(4D Server log recording;1) //server side - on a client:
SET DATABASE PARAMETER(Client Log Recording;1) //remote side
Note: This statement also starts the 4DRequestsLog_ProcessInfo.txt log file (see below).
Headers
This file starts with the following headers:
- Log Session Identifier
- Hostname of the server that hosts the application
- User Login Name: login on the OS of the user that ran the 4D application on the server.
Contents
For each request, the following fields are logged:
| Field name | Description |
| sequence_number | Unique and sequential operation number in the logging session |
| time | Date and time using ISO 8601 format: 'YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS.sss' |
| systemid | System ID |
| component | Component signature (e.g., '4SQLS' or 'dbmg') |
| process_info_index | Corresponds to the "index" field in 4DRequestsLog_ProcessInfo.txt log, and permits linking a request to a process. |
| request | Request ID in C/S or message string for SQL requests or LOG EVENT messages |
| bytes_in | Number of bytes received |
| bytes_out | Number of bytes sent |
| server_duration | exec_duration | Depends on where the log is generated:
|
| write_duration | Time taken in microseconds for sending the:
|
| task_kind | Preemptive or cooperative (respectively 'p' or 'c') |
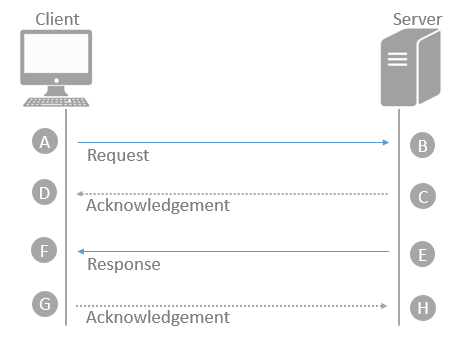
| rtt | Time estimate in microseconds for the client to send the request and the server to acknowledge it. A to D and E to H in image below.
|
Request flow:
This log file records information on each process created on the 4D Server machine or the 4D remote machine that executed the command (excluding Web requests).
How to start this log:
- on the server:
SET DATABASE PARAMETER(4D Server log recording;1) //server side - on a client:
SET DATABASE PARAMETER(Client Log Recording;1) //remote side
Note: This statement also starts the 4DRequestsLog.txt log file (see above).
Headers
This file starts with the following headers:
- Log Session Identifier
- Hostname of the server that hosts the application
- User Login Name: login on the OS of the user that ran the 4D application on the server.
Contents
For each process, the following fields are logged:
| Field name | Description |
| sequence_number | Unique and sequential operation number in the logging session |
| time | Date and time using ISO 8601 format: "YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS.sss" |
| process_info_index | Unique and sequential process number |
| CDB4DBaseContext | DB4D component database context UUID |
| systemid | System ID |
| server_process_id | Process ID on Server |
| remote_process_id | Process ID on Client |
| process_name | Process name |
| cID | Identifier of 4D Connection |
| uID | Identifier of 4D Client |
| IP | Client IPv4/IPv6 address |
| host_name | Client hostname |
| user_name | User Login Name on client |
| connection_uuid | UUID identifier of process connection |
| server_process_unique_id | Unique process ID on Server |
This log file records each HTTP request and each response in raw mode. Whole requests, including headers, are logged; optionally, body parts can be logged as well.
How to start this log:
WEB SET OPTION(Web debug log;wdl enable without body) //other values are availableThe following fields are logged for both Request and Response:
| Field name | Description |
| SocketID | ID of socket used for communication |
| PeerIP | IPv4 address of host (client) |
| PeerPort | Port used by host (client) |
| TimeStamp | Timestamp in milliseconds (since system startup) |
| ConnectionID | Connection UUID (UUID of VTCPSocket used for communication) |
| SequenceNumber | Unique and sequential operation number in the logging session |
This log file records each event occurring at the 4D programming level. Standard mode provides a basic view of events.
How to start this log:
SET DATABASE PARAMETER(Debug Log Recording;2) //standard, all processes
SET DATABASE PARAMETER(Current process debug log recording;2) //standard, current process onlyThe following fields are logged for each event:
| Column # | Description |
| 1 | Unique and sequential operation number in the logging session |
| 2 | Elapsed time in milliseconds since log startup |
| 3 | Process ID (p=xx) and unique process ID (puid=xx) |
| 4 | Stack level |
| 5 | Can be Command Name/ Method Name/Message/ Task Start Stop info/Plugin Name, event or Callback/Connection UUID |
| 6 | Time taken for logging operation in milliseconds (different from 2nd column) |
This log file records each event occurring at the 4D programming level in a tabbed, compact format that includes additional information (compared to the standard format).
How to start this log:
SET DATABASE PARAMETER(Debug Log Recording;2+4) //extended tabbed format, all processes
SET DATABASE PARAMETER(Current process debug log recording;2+4) //extended, current process onlyThe following fields are logged for each event:
| Column # | Description | |||||||||
| 1 | Unique and sequential operation number in the logging session | |||||||||
| 2 | Elapsed time since log startup in "hh:mm:ss:ms" format (can be preceded by a day counter. For example, if the log was started 3 days ago, the time could be "3+11:58:23:163") | |||||||||
| 3 | Process ID | |||||||||
| 4 | Unique process ID | |||||||||
| 5 | Stack level | |||||||||
| 6 | May represent (depending on type entry logged in the 8th column):
| |||||||||
| 7 | Parameters passed to commands, methods, or plugins | |||||||||
| 8 | Log operation type. This value may be an absolute value:
| |||||||||
| 9 | Form event if any; empty in other cases (suppose that column is used when code is executed in a form method or object method) | |||||||||
| 10 | Elapsed time in micro seconds of the current logged action; only for the closing stack levels (see 10th columns in lines 123 and 124 in the log above) |
This log file records each exchange between the 4D application and the SMTP server. The file can be produced in two versions:
- a regular version: named 4DSMTPLog.txt, no attachments, uses an automatic circular file recycling each 10 MB; intended for usual debugging.
To start this log:
SET DATABASE PARAMETER(SMTP Log;1) //start smtp log
- 4D Server: Click on the Start Request and Debug Logs button in the Maintenance Page of the 4D Server administration window.
- an extended version: attachment(s) included, no automatic recycling; reserved for specific purposes.
To start this log:$server:=New object
...
$server.logFile:="MySMTPAuthLog.txt"
$transporter:=SMTP New transporter($server)
Contents
For each request, the following fields are logged:
| Column # | Description |
| 1 | Unique and sequential operation number in the logging session |
| 2 | Date and time in RFC3339 format (yyyy-mm-ddThh:mm:ss.ms) |
| 3 | 4D Process ID |
| 4 | Unique process ID |
| 5 |
|
*Warning: MIME contents (attachments) can represent a large quantity of data. Make sure you have enough disk space to save these data.
This log records each ORDA request sent from a remote machine. You can direct log information to memory or to a file on disk. The name and location of this log file are your choice.
How to start this log:
//to be executed on a remote machine
ds.startRequestLog(File("/PACKAGE/Logs/ordaLog.txt")) //can be also sent to memoryNote: If you want to use the unique sequence number in ORDA request log, you need to trigger it:
//to be executed on a remote machine
SET DATABASE PARAMETER(Client Log Recording;1) //to enable log sequence number
ds.startRequestLog(File("/PACKAGE/Logs/ordaLog.txt")) //can be also sent to memory
SET DATABASE PARAMETER(Client Log Recording;0) //disabling sequence numberThe following fields are logged for each request:
| Field name | Description | Example |
| sequenceNumber | Unique and sequential operation number in the logging session | 104 |
| url | Client ORDA request URL | "rest/Persons(30001)" |
| startTime | Starting date and time using ISO 8601 format | "2019-05-28T08:25:12.346Z" |
| endTime | Ending date and time using ISO 8601 format | "2019-05-28T08:25:12.371Z" |
| duration | Client processing duration (ms) | 25 |
| response | Server response object | {"status":200,"body":{"__entityModel":"Persons",[...] |
Product: 4D
Theme: Debug log files
Modified: 4D v17 R5
Modified: 4D v17 R6
4D Design Reference ( 4D v18)