4D v14.3
Description of formula editor
- 4D Design Reference
-
- Formula editor
-
- Access to formula editor
- Description of formula editor
 Description of formula editor
Description of formula editor
The Formula editor provides many shortcuts for writing formulas. You can click field names, operators and commands, as well as any project methods, to add them to the formula. When you click on an item, it is automatically displayed in the editing area where you can then modify it using standard cut/copy/paste functions. You can also enter items directly in the editing area or drag and drop them from the list of items.
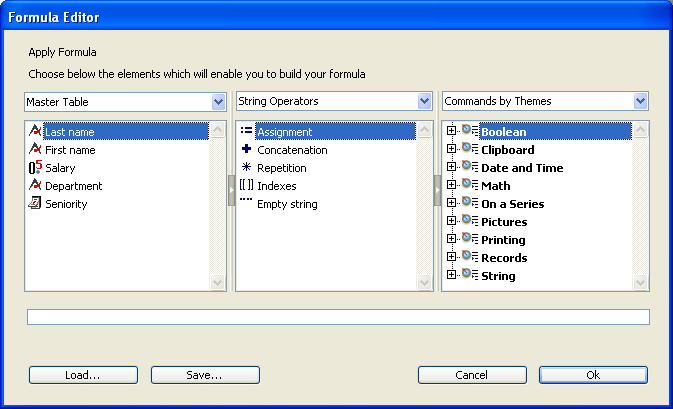
The Formula editor contains the following areas:
- List of tables and fields: This area displays the fields of the table. The menu located above the list lets you set the fields to be displayed. You can use fields of the current table, those of related tables or those of all the tables.
Note: Tables and fields with the Invisible property do not appear in the list. For more information about this property, refer to the “Attributes” section in Table properties and Field properties. - Operators list: The operators list lets you choose the operators to be used in the formula. The operators are grouped into themes found in the menu located above the list:
Each theme displays all the available operators for the corresponding type of data or operation. For example, the assignment operator := is available for all data types. For a description of each operator, refer to the following section. - Commands list: The commands list contains the 4D functions that can be used in formulas, as well as any project methods allowed by the developer. The menu located above the list lets you display the commands by theme or by alphabetical order. Refer to the 4D Language Reference manual for a description of the 4D commands that appear in this menu.
In principle, project methods that can be used in formulas must be declared beforehand using the 4D SET ALLOWED METHODS command. However, by default, the Designer and Administrator of the database have complete access to the 4D commands and user methods in the Formula editor. It is also possible to completely disable access control for all users. These options are set on the Security page of the Database settings.
Here is a brief description of the different operators available in the Formula editor. For a more detailed description of the possibilities provided by these operators, refer to the Operators chapter of the 4D Language Reference manual.
- String Operators
A and B are character strings; N is a number.Operator Use Description := Assignment A:=B Assigns the value B to A + Concatenation A+B Returns AB * Repetition A*N Repeats the value of A N times [[ ]] Indexes [[A]]N Returns the Nth character of A "" Empty string "" Inserts a pair of quotation marks
- Numeric Operators
X and Y are numbers.Operator Use Description := Assignment X:=Y Assigns the value Y to X + Addition X+Y Returns X plus Y - Subtraction X-Y Returns X minus Y * Multiplication X*Y Returns X multiplied by Y / Division X/Y Returns X divided by Y \ Integer Division X\Y Returns the integer division of X by Y (X and Y must be integers) % Modulo X%Y Divides X by Y and returns the remainder ^ Exponentiation X^Y Returns X to the power of Y
Note: The modulo % operator returns significant values with numbers belonging to the long integer category (from -2^31 to +2^31 minus 1). To calculate the modulo of numbers outside of this interval, use the Mod command.
- Date Operators
D1 and D2 are dates; N is a number.Operator Use Description := Assignment D1:=D2 Assigns the value D2 to D1 + Addition D1+N Returns D1 plus N days - Difference D1-D2 or Returns the number of days between D1 and D2 D1-N Returns D1 minus N days !//! Blank date !00/00/00! Inserts a blank date
- Time Operators
H1 and H2 are times; N is a number.
Operator Use Description := Assignment H1:=H2 Assigns the value H2 to H1 + Addition H1+H2 or Returns H1 plus H2 H1+N Returns H1 plus N seconds, expressed in seconds elapsed since midnight - Subtraction H1-H2 or Returns H1 minus H2 H1-N Returns H1 minus N seconds, expressed in seconds elapsed since midnight * Multiplication H1*N Returns H1 multiplied by N, expressed in seconds elapsed since midnight / Division H1/N Returns H1 divided by N, expressed in seconds elapsed since midnight \ Integer Division H1\N Returns the integer division of H1 by N, expressed in seconds elapsed since midnight % Modulo H1%N Divides H1 by N and returns the remainder ?::? Blank hour ?00:00:00? Inserts a blank hour
- Comparison Operators
Z1 and Z2 can be of the string, numeric, date or time type.Operator Use Description = Equal Z1=Z2 Returns True if Z1 equals Z2 # Not equal Z1#Z2 Returns True if Z1 does not equal Z2 > Greater than Z1>D Returns True if Z1 is greater than Z2 >= Greater than or equal to Z1>=Z2 Returns True if Z1 is greater than or equal to Z2 < Less than Z1<Z2 Returns True if Z1 is less than Z2 <= Less than or equal to Z1<=Z2 Returns True if Z1 is less than or equal to Z2
- Logical Operators
B1 and B2 must be Booleans (expressions that are TRUE or FALSE)
Operator Use Description & AND B1 & B2 Returns True if B1 is True and B2 is True | OR B1 | B2 Returns True if B1 is True or B2 is True
Product: 4D
Theme: Formula editor
4D Design Reference ( 4D v14 R2)
4D Design Reference ( 4D v13.4)
4D Design Reference ( 4D v14 R3)
4D Design Reference ( 4D v14.3)
4D Design Reference ( 4D v14 R4)
Parent of : Description of formula editor ( 4D v12.4)







